4 min read
Demystifying Edge Computing: Part 2 – What is the EDGE
Edge Computing IoT, more specifically for this post, IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) is probably the hottest buzzword today. The whole...
Build intelligent, data-driven capabilities that turn raw information into insights, automation, and smarter decision-making across your organization.
Modernize, secure, and operationalize your cloud environment with solutions that strengthen resilience, reduce risk, and improve IT performance.
Deliver modern applications and connected IoT solutions that enhance operations, streamline workflows, and create seamless digital experiences.
High-impact IT project execution from planning to delivery, aligned with business goals and designed for predictable outcomes.
Structured change management and M&A support that helps teams adapt, reduce disruption, and successfully navigate complex transitions.
Cloud-first IT operations that streamline cost, strengthen security, and provide modern, scalable infrastructure for growing teams.
1 min read
Admin : January 7, 2026
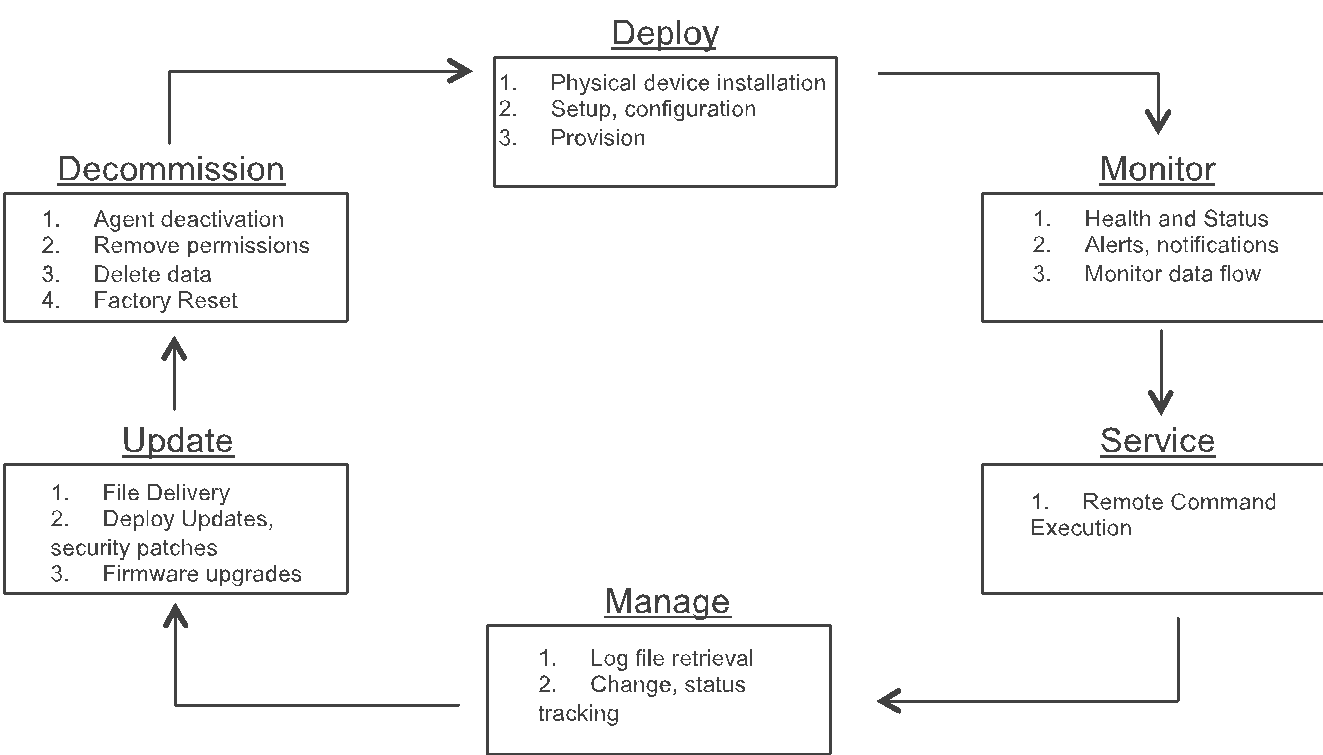
In our earlier post we’ve touched on this point a few times, so let’s dig a little deeper into device management. In the context of IoT, you really need to consider the total number of devices you are planning on managing, monitoring, etc. The examples I gave above are pretty straightforward and very minimal, but how would you scale that across 1000s of PLCs and/or sensors, etc.? How would you know if one of your 1000+ sensors needed a new battery or has become faulty? Although there is a change management component required, I am only going to focus on what technology can do for you, specifically device management software.
Device management software will provide the process for deploying, provisioning, authenticating, configuring, and monitoring devices, as well as maintaining firmware and software that provides functional capabilities on the physical device.
Ideally, the device management software would include the following functionality:
Commissioning, provisioning, and authentication: Provide the device with an authenticated identity and set of credentials that it uses to communicate with other devices, apps, and services.
Security: Considerations for both physical tampering and network-borne threats
Monitoring and diagnostics: Ability to remotely login into the device, view logs, setup rules, track firmware, location, status, and device capabilities
Integration: The ability to integrate into other enterprise applications without the need for custom development
Updates and upgrades: At scale, be able to update firmware and install patches
Decommissioning: Revoking any identities associated with the device so that it is no longer able to communicate with other devices, apps or services within the system
2 min read
Analytics at the Edge, Fog and Cloud We have spoken about edge, fog and to a much lesser degree cloud computing. Each of them have pros and...
2 min read
Edge Computing – Examples using Google Interestingly enough, edge computing typically is related to an IoT project; IoT solutions become Big...